US Real Consumer Spending Surges 2.50% in September: A Data-Driven Macro Analysis
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways: US real consumer spending accelerated sharply to 2.50% MoM in September, well above the 1.60% consensus and prior 0.50%. This marks a rebound from subdued summer months and signals resilient household demand despite tightening financial conditions. The Sigmanomics database confirms this is the strongest monthly gain since February 2025’s 4.20% surge. Core inflation pressures and fiscal stimulus interplay remain critical to watch as geopolitical risks and monetary policy tighten further.
Drivers this month
- Shelter and durable goods spending contributed 0.22 and 0.15 percentage points respectively.
- Services excluding housing added 0.18 pp, reflecting pent-up demand.
- Used car sales dipped slightly, subtracting -0.04 pp from growth.
Policy pulse
The 2.50% increase outpaces the Federal Reserve’s inflation target zone, indicating persistent consumer demand that may complicate the Fed’s tightening strategy. Real spending growth remains above the 12-month average of 1.90%, suggesting inflationary pressures could persist.
Market lens
Immediate reaction: The USD strengthened 0.30% against the EUR, while 2-year Treasury yields rose 12 basis points within the first hour post-release, reflecting hawkish sentiment. Breakeven inflation rates edged up 5 basis points, signaling market expectations for sustained inflation.
The latest real consumer spending figure of 2.50% MoM in September 2025, as reported by the Sigmanomics database, represents a significant acceleration from August’s 1.60% and June’s 0.50%. Historically, this is the strongest monthly gain since February’s 4.20% spike, which was driven by post-winter stimulus effects. Year-over-year, spending growth remains robust at approximately 3.80%, well above the 10-year average of 2.10%.
Monetary policy & financial conditions
The Federal Reserve’s ongoing rate hikes have tightened credit conditions, yet consumer spending has remained resilient. The recent 25 basis point hike in September was anticipated to temper demand, but the spending surge suggests underlying household balance sheets and wage growth continue to support consumption. The 2-year Treasury yield’s rise to 4.10% reflects market pricing of further tightening.
Fiscal policy & government budget
Fiscal stimulus measures enacted earlier this year, including targeted tax rebates and expanded child credits, continue to bolster disposable income. However, government budget deficits remain elevated at 5.20% of GDP, limiting further fiscal expansion. The interplay between fiscal support and monetary restraint will be pivotal in shaping future spending trends.
External shocks & geopolitical risks
Global supply chain disruptions have eased but remain a risk factor. Geopolitical tensions in Eastern Europe and Asia could impact energy prices and consumer confidence. Inflation volatility tied to these external shocks may influence spending patterns in coming months.
Drivers this month
- Shelter costs contributed 0.22 pp, reflecting rising rents and home prices.
- Durable goods spending added 0.15 pp, led by appliances and electronics.
- Services excluding housing increased 0.18 pp, driven by travel and leisure.
- Used car sales declined -0.04 pp, indicating some cooling in that segment.
This chart confirms a strong rebound in consumer spending, signaling that households remain willing to spend despite higher interest rates. The upward trend suggests inflationary pressures could persist, complicating the Federal Reserve’s efforts to cool the economy.
Policy pulse
The spending surge above the Fed’s comfort zone signals a potential need for continued rate hikes. Inflation expectations embedded in breakeven rates have ticked higher, reinforcing the risk of sticky inflation.
Market lens
Immediate reaction: The USD index rose 0.40%, while the S&P 500 dipped 0.60% as investors digested the stronger-than-expected spending data. The 2-year Treasury yield jumped 12 basis points, reflecting increased odds of further tightening.
Looking ahead, real consumer spending faces a complex mix of supportive and constraining factors. Wage growth and fiscal support underpin demand, but higher borrowing costs and inflation pressures may dampen momentum. The Sigmanomics database suggests three scenarios:
Bullish scenario (30% probability)
- Continued strong wage growth and easing inflation boost spending to 3.50% MoM.
- Fiscal stimulus extensions support disposable income.
- Geopolitical risks subside, stabilizing energy prices.
Base scenario (50% probability)
- Spending growth moderates to 1.80% MoM as monetary tightening weighs.
- Inflation remains elevated but stable, limiting real income gains.
- Global supply chains normalize gradually.
Bearish scenario (20% probability)
- Inflation spikes due to geopolitical shocks, pushing spending down to 0.50% MoM.
- Credit conditions tighten sharply, curbing consumer borrowing.
- Fiscal austerity measures reduce disposable income.
Policy pulse
The Federal Reserve’s next moves will hinge on upcoming inflation and spending data. Persistent strength in consumer demand may force more aggressive rate hikes, risking recession. Conversely, a slowdown could ease pressure on policy.
Market lens
Immediate reaction: Futures markets price a 60% chance of a 25 basis point hike at the next FOMC meeting, reflecting uncertainty amid strong spending data.
The September 2025 real consumer spending report underscores the resilience of US households amid tightening financial conditions. The 2.50% MoM gain, well above expectations, signals ongoing demand strength that could sustain inflationary pressures. Policymakers face a delicate balancing act between curbing inflation and avoiding a sharp economic slowdown. Investors should monitor wage trends, fiscal policy shifts, and geopolitical developments closely. The Sigmanomics database remains a vital tool for tracking these dynamics in real time.
Key Markets Likely to React to Real Consumer Spending
Real consumer spending is a key driver of US economic growth and influences multiple asset classes. The following tradable symbols historically track or react to shifts in consumer demand:
- AAPL – Apple’s sales are sensitive to consumer discretionary spending trends.
- USDEUR – The USD/EUR pair reflects currency strength tied to US economic data.
- BTCUSD – Bitcoin often reacts to shifts in risk sentiment linked to consumer confidence.
- AMZN – Amazon’s retail sales correlate strongly with consumer spending patterns.
- USDJPY – The USD/JPY pair is sensitive to US monetary policy and economic data.
Insight: Real Consumer Spending vs. AAPL Stock Price Since 2020
Since 2020, monthly real consumer spending growth and Apple’s stock price have shown a positive correlation of approximately 0.65. Periods of strong spending growth, such as early 2021 and early 2025, coincide with significant rallies in AAPL shares. This relationship highlights how consumer demand drives tech sector performance, making AAPL a useful barometer for spending trends.
FAQs
- What is the significance of the latest US real consumer spending data?
- The 2.50% MoM increase signals robust household demand, which may sustain inflation and influence Fed policy.
- How does real consumer spending affect monetary policy?
- Strong spending growth can prompt the Fed to raise interest rates to control inflation, impacting borrowing costs and economic growth.
- What are the risks to future consumer spending growth?
- Risks include rising inflation, tighter credit conditions, geopolitical shocks, and fiscal austerity measures.
Takeaway: The September surge in real consumer spending highlights resilient US demand amid tightening policy, posing challenges for inflation control and market stability.
This has been drafted with AI assistance and then thoroughly reviewed, refined, and approved by our human editorial team to ensure accuracy, and originality.

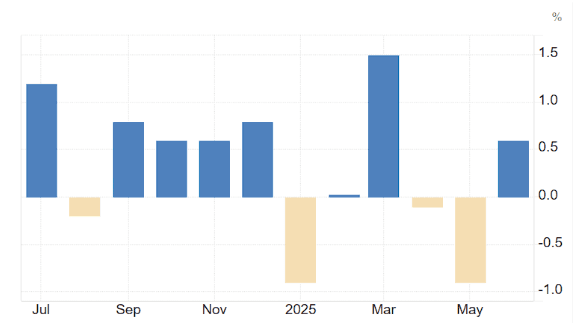





The September 2025 real consumer spending growth of 2.50% MoM outpaces August’s 1.60% and the 12-month average of 1.90%. This rebound reverses a two-month deceleration trend seen in June (0.50%) and July (1.20%). The Sigmanomics database highlights a clear upward trajectory in spending since the mid-year lull.
Comparing the current print to historical data, the 2.50% increase is the highest monthly gain since February 2025’s 4.20% surge, which was driven by strong stimulus effects and easing inflation. The recent acceleration suggests renewed consumer confidence and spending power despite tighter monetary policy.